What is the Difference Between G1 and G2 Phase of Cell Cycle Biology Diagrams The G 2 /M phase is necessarily a transient state in which the morphology of the plasma membrane becomes analogous to a bicontinuous cubic phase (Fig. 7) [31,32,77,78]. This type of lipid assembly has been reviewed in some detail recently [79,80] , including its relevance to biological systems [30,81,82] .
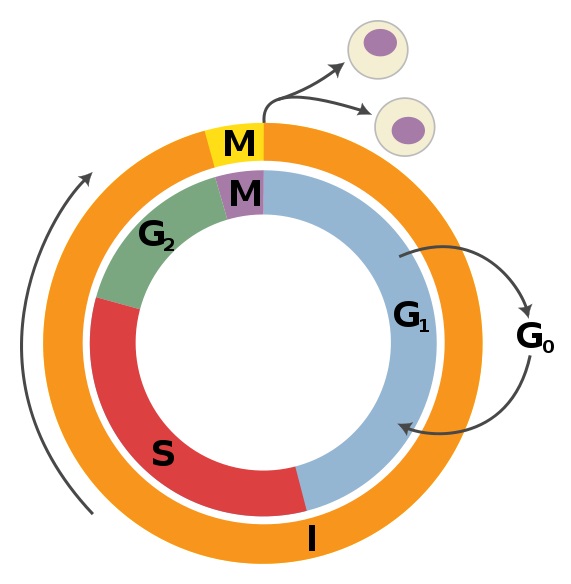
The G2 phase is the third stage of the cell cycle that occurs after DNA replication and before mitosis. During this phase, the cell prepares for division by undergoing critical processes such as repairing any DNA damage, synthesizing proteins, and ensuring that all cellular components are ready for mitosis. The G2 phase plays a key role in maintaining genetic integrity and allowing for proper
The G2 Phase: Preparing for Cell Division Biology Diagrams
Importantly, this phase ensures that everything is in place for DNA synthesis to occur in the next phase. S Phase (Synthesis): During this phase, the cell's DNA replicates. At the end of the S phase, each chromosome consists of two chromatids attached at the centromere. G2 Phase (Gap 2): Here, the cell continues growing and prepares for Cell growth is central to the cell cycle, and this is the primary purpose of interphase. At the end of this phase, there is double the amount of DNA, centrioles have replicated, and the cell is big enough for cell division. Interphase consists of the first growth (G1 phase), Synthesis (S phase), and the second growth (G2 phase) phases (figure 1

The cell cycle consists of a timed sequence of events that occur during interphase and mitosis (M). Interphase is made up of the G 1 (G = gap) phase, the S (synthesis) phase, and the G 2 phase (Fig. 15-2).Both G phases contain checkpoints that govern whether the cell moves into DNA replication (G 1 checkpoint) or into mitosis (G 2 checkpoint).. The G 1 and G 2 phases involve the synthesis of

Cell Cycle G2 Phase - an overview Biology Diagrams
G 2 Phase. In the G 2 phase, or second gap, the cell replenishes its energy stores and synthesizes the proteins necessary for chromosome manipulation. Some cell organelles are duplicated, and the cytoskeleton is dismantled to provide resources for the mitotic spindle. There may be additional cell growth during G 2.The final preparations for the mitotic phase must be completed before the cell
