Cell cycle on the crossroad of tumorigenesis and cancer therapy Trends Biology Diagrams Example of inhibitors that, in early clinical trials, are targeting cyclin-dependent kinases (cdk s) acting in or outside of the cell cycle.Inhibitors of cdk also inhibit transcription. A key enzyme in the transcription machinery, rna polymerase ii, is phosphorylated by several cdk s 34, 35.The most important regulator is cdk 9/cyclin T. Inhibition of cdk 9/cyclin T by a cdki such as

The cell cycle blockade imposed by CDK4/CDK6 inhibitors is not necessarily irreversible 64,66, and this may contribute to disease progression not only upon the recovery of tumour cell
cycle inhibitors for cancer therapy Biology Diagrams
Keywords: cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors, cancer, cell cycle, CDKs, CDK inhibitors. 1. Cyclin-Dependent Kinases (CDKs) Protein phosphorylation is a necessary mechanism to drive numerous cellular processes such as cell division, migration, differentiation and programmed cell death. This process is regulated by many enzymes, including cyclin

Decision to enter the cell cycle. The E2F inhibitor RB plays a central role in the 'decision' to enter a new cell cycle 2,3. During the prereplicative G1 phase, RB keeps E2F-dependent
Cell Cycle Control System: Key Phases and Proteins Biology Diagrams
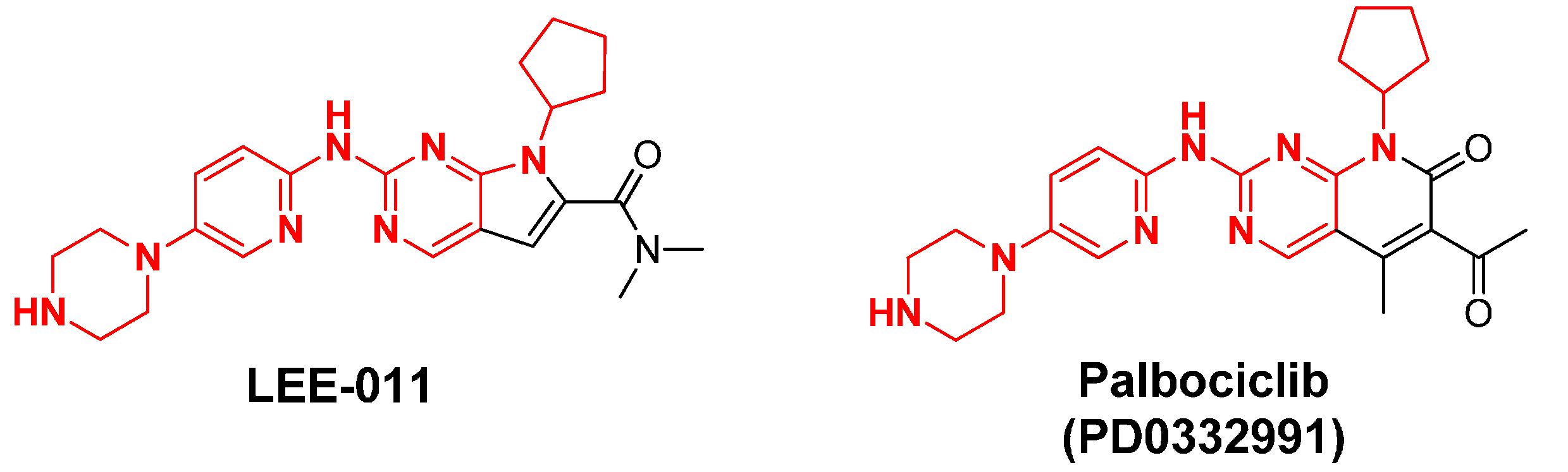
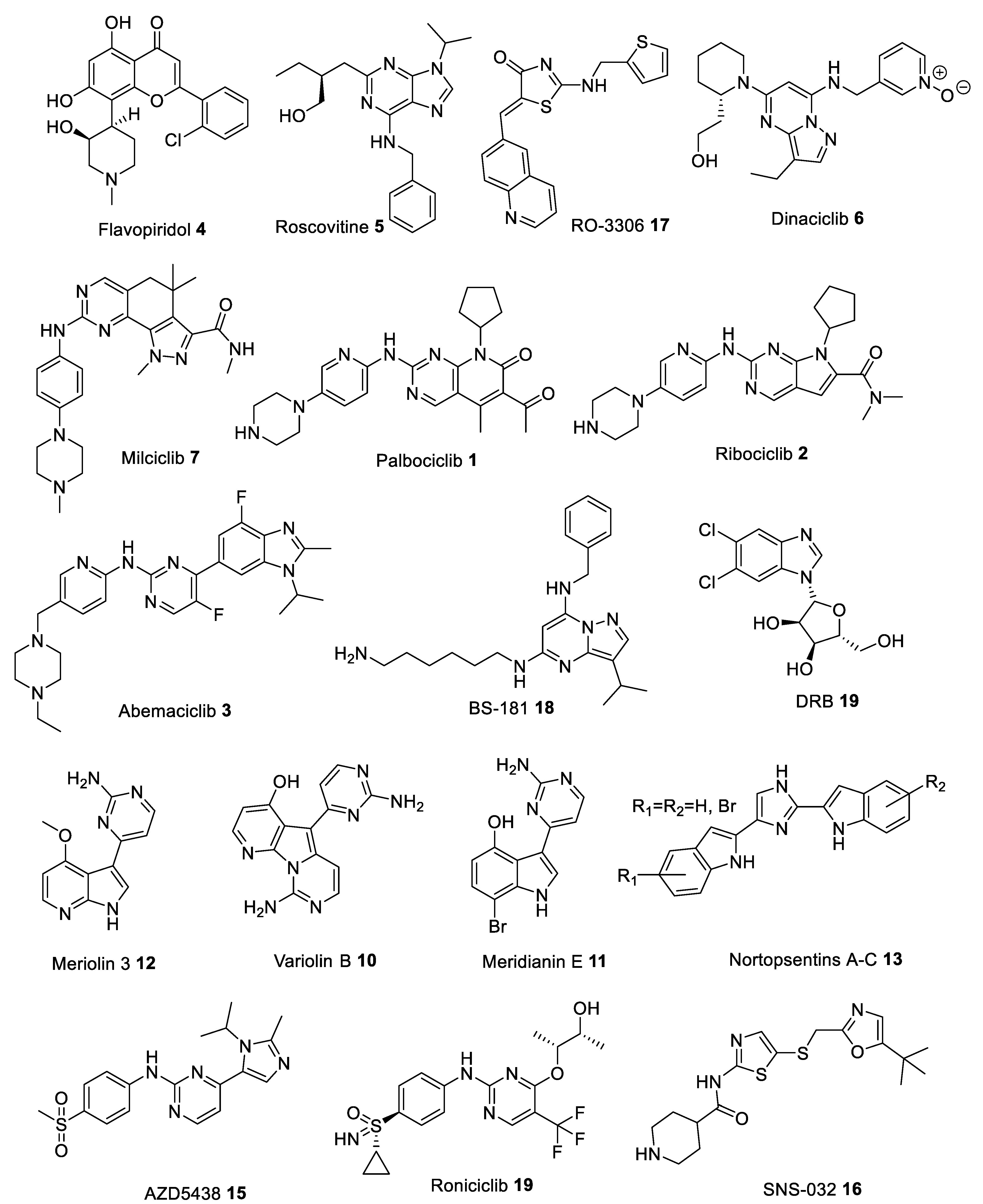
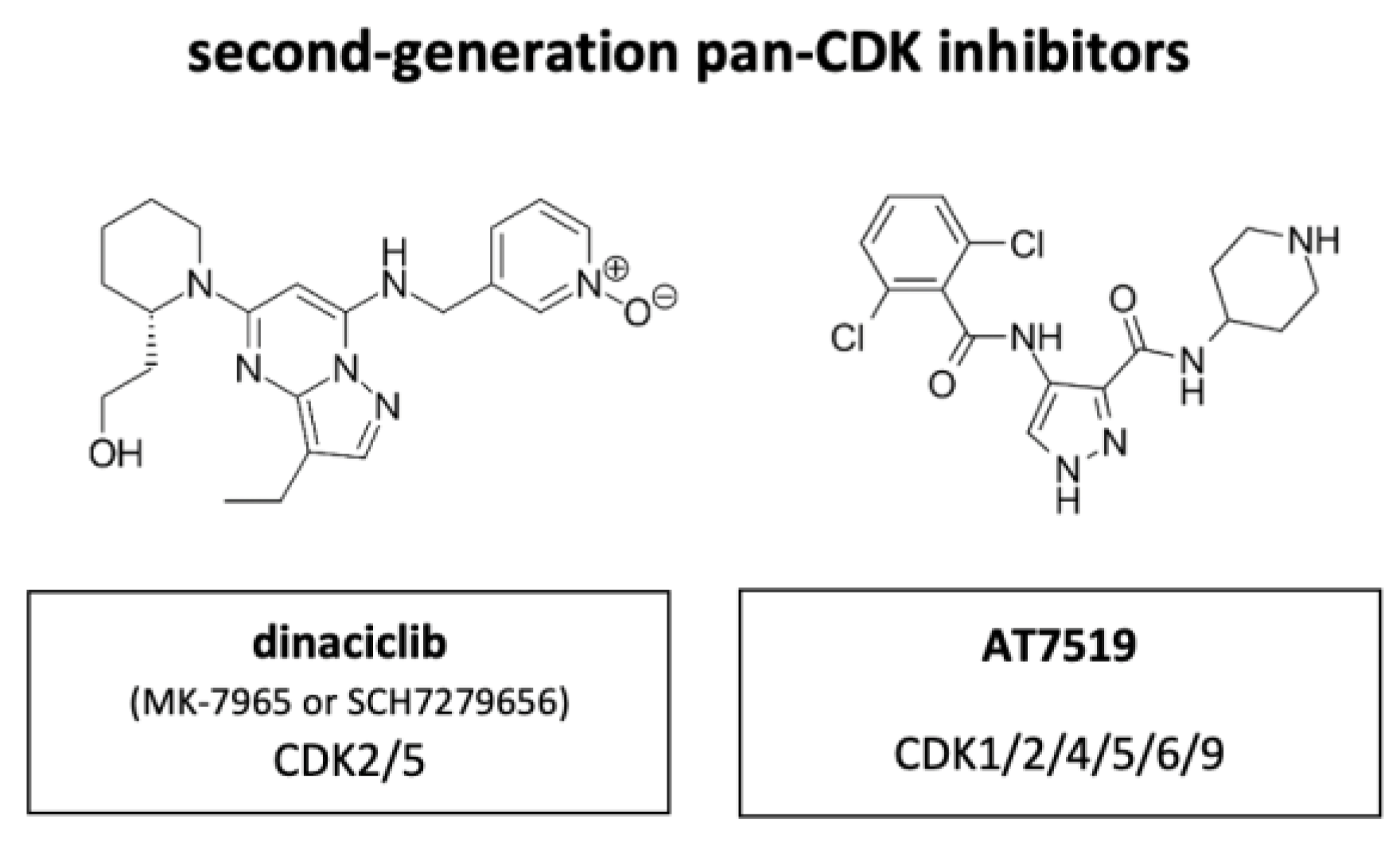
CDK inhibitors have been studied since the 1990s. The first generation of CDK inhibitors are pan-CDK inhibitors, including Flavopiridol and Roscovitine, etc. The main function of these inhibitors is to block cell cycle and inhibit cell proliferation by inhibiting the CDK enzyme activity. Cell cycle inhibitors prevent unchecked proliferation by inhibiting CDKs. These inhibitors fall into two families: INK4 (p15, p16, p18, p19) and Cip/Kip (p21, p27, p57). INK4 proteins inhibit CDK4 and CDK6, blocking cyclin D interaction and preventing G1 progression. Cip/Kip proteins have broader specificity, inhibiting multiple CDKs and